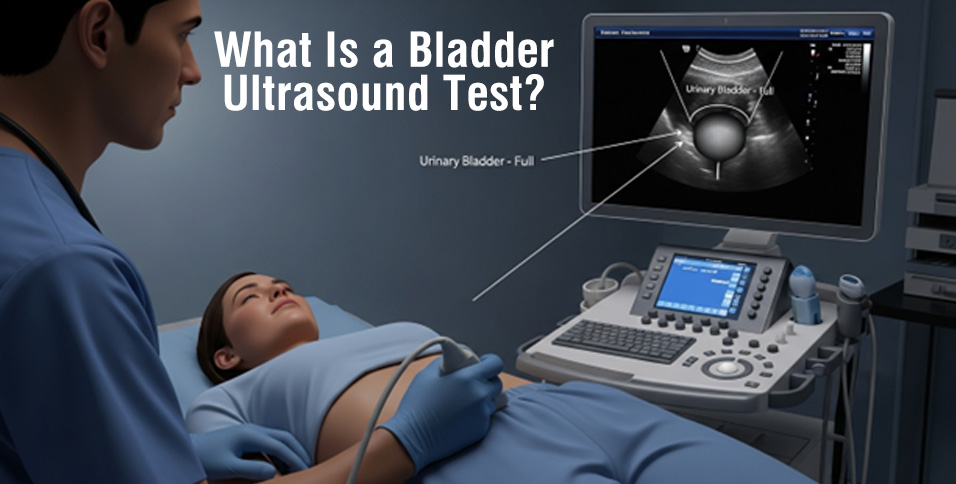
A bladder ultrasound test, often referred to as a bladder scan, is a non-invasive diagnostic imaging procedure used by healthcare professionals to evaluate bladder health and overall urinary function. This test is commonly recommended when patients experience urinary symptoms such as pelvic pain, difficulty urinating, frequent urination, weak urine flow, or the feeling that the bladder does not empty completely after urination.
A bladder ultrasound test helps doctors examine the bladder without the need for surgery, needles, or radiation. Because of its safety, simplicity, and accuracy, it is frequently used as a first-line diagnostic tool in both hospitals and outpatient clinics.
The primary goal of a bladder ultrasound test is to measure the volume of urine in the bladder and assess its structure. It allows clinicians to determine whether urine is being retained after voiding and whether the bladder walls appear normal. One of the biggest advantages of this test is that it is quick, safe, and completely painless.
Patients are usually asked to keep their bladder full before the scan, as a full bladder provides clearer imaging and more reliable measurements. In most cases, no special preparation is required beyond drinking water prior to the test.
Equipment Used in a Bladder Ultrasound Test
A bladder ultrasound test relies on specialized medical equipment designed to capture clear and accurate images of the bladder. The main components include the following:
Bladder Scanner
A bladder scanner is a portable, hand-held ultrasound device that creates a virtual 3D image of the bladder and calculates urine volume within seconds. Modern bladder scanner devices are widely used in hospitals, clinics, and long-term care facilities because of their accuracy, ease of use, and ability to provide instant results.
These devices are especially useful in bedside care, as they help medical staff assess bladder function without the need for invasive catheterization. The compact design and user-friendly interface make bladder scanners an essential tool in modern healthcare settings.
Monitor
The monitor displays high-quality 3D images generated by the bladder scanner. These images allow healthcare professionals to analyze bladder size, shape, wall thickness, and urine retention. Clear visualization helps clinicians make informed decisions regarding diagnosis and treatment.
How Bladder Scanners Work
Bladder scanners operate using ultrasound technology, which relies on sound waves rather than radiation. Inside the device are transducers that emit high-frequency sound waves into the lower abdomen. When these sound waves reach the bladder, they bounce back toward the scanner.
The returning sound waves are converted into digital data, which the system processes to generate detailed images of the bladder. These images can be taken before and after urination, allowing clinicians to measure how much urine remains in the bladder after voiding.
The collected data is transmitted to a computer system and displayed on the monitor in real time. Doctors, nurses, and radiologists interpret this information to assess bladder function, identify abnormalities, and determine the best course of treatment.
Today, advanced bladder scanner solutions—such as those available at BladGo
are designed to deliver fast, accurate, and reliable bladder assessments. These modern devices help reduce patient discomfort, minimize human error, and significantly lower the need for invasive diagnostic procedures.
Preparation Before a Bladder Ultrasound Test
In most cases, preparation for a bladder ultrasound test is minimal. Patients are typically instructed to drink several glasses of water before the procedure and avoid urinating until the scan is completed. A full bladder helps ensure accurate imaging and precise measurement of urine volume.
Patients may also be advised to wear comfortable clothing to allow easy access to the lower abdomen. Specific instructions can vary depending on the healthcare provider, but overall preparation is simple and stress-free.
What Happens During the Procedure?
During the procedure, the patient lies comfortably on an examination table. A clear, water-based gel is applied to the lower abdomen to help transmit ultrasound waves effectively. The technician then moves the bladder scanner over the area.
The scan itself usually takes between 10 and 20 minutes. Patients may feel mild pressure from the device, but the procedure is not painful. Once imaging is complete, patients are typically allowed to urinate, and in some cases, a second scan may be performed to measure post-void residual urine.
There is no recovery time needed, and patients can return to their normal activities immediately after the test.
Why Are Bladder Ultrasound Tests Done?
Bladder ultrasound tests are commonly performed to diagnose a wide range of bladder dysfunctions. One of the most frequent conditions identified through this test is urinary incontinence, which refers to the inability to control urine storage or release. According to the Urology Care Foundation, nearly one-third of men and women in the United States experience some form of urinary incontinence.
Other common reasons for performing a bladder ultrasound test include overactive bladder (OAB), urinary retention, recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs), pain or discomfort during urination, difficulty starting or stopping urine flow, monitoring bladder function after surgery, and evaluating bladder problems related to neurological conditions.
Early diagnosis through bladder ultrasound testing allows healthcare providers to address issues promptly, reduce complications, and improve patient outcomes.
Where Bladder Ultrasound Tests Are Performed
Bladder ultrasound tests are widely used in acute care settings where rapid diagnosis and short-term treatment are required. Emergency departments often rely on bladder scanners to quickly assess urinary retention or bladder trauma.
They are also commonly performed in long-term care facilities, rehabilitation centers, urology clinics, gynecology practices, and outpatient diagnostic centers. In these environments, bladder scanners help improve workflow efficiency and patient comfort.
In many healthcare settings, nurses use bladder scanner devices directly at the bedside. This practice reduces unnecessary catheterization, lowers the risk of infection, and enhances patient safety. The ability to perform quick, non-invasive assessments makes bladder scanners a valuable tool across multiple medical disciplines.
Benefits of a Bladder Ultrasound Test
Some key benefits of a bladder ultrasound test include being non-invasive and painless, having no exposure to radiation, delivering quick and accurate results, being suitable for patients of all ages, reducing the need for invasive procedures, and improving overall patient comfort and safety.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a bladder ultrasound test is a safe, painless, and non-invasive diagnostic tool that plays a vital role in identifying common bladder conditions. By using advanced bladder scanner technology, healthcare providers can accurately measure urine volume, assess bladder structure, and detect dysfunctions early.
This test helps clinicians diagnose symptoms such as urinary incontinence, urine leakage, urinary retention, frequent urination, and painful urination with greater confidence. If you are experiencing ongoing bladder-related symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional and consider a bladder ultrasound test for proper evaluation.
With the help of modern bladder scanner devices, clinicians can ensure accurate diagnosis, reduce patient discomfort, and deliver better overall patient care.